Basic fibroblast growth factor (FGF2, bFGF) is the most extensively studied member of the FGF family and is involved in neurogenesis, differentiation, neuroprotection, and synaptic plasticity in the CNS. FGF2 executes its pleiotropic biologic actions by binding, dimerizing, and activating FGF receptors (FGFRs). The present study reports the physiologic impact of various FGF2-FGFR1 contact sites employing three different synthetic peptides, termed canofins, designed based on structural analysis of the interactions between FGF2 and FGFR1. Canofins mimic the cognate ligand interaction with the receptor and preserve the neuritogenic and neuroprotective properties of FGF2. Canofins were shown by surface plasmon resonance analysis to bind to FGFR1 and promote receptor activation. However, FGF2-induced receptor phosphorylation was inhibited by canofins, indicating that canofins are partial FGFR agonists. Furthermore, canofins were demonstrated to induce neuronal differentiation determined by neurite outgrowth from cerebellar granule neurons, and this effect was dependent on FGFR activation. Additionally, canofins acted as neuroprotectants, promoting survival of cerebellar granule neurons induced to undergo apoptosis. Our results suggest that canofins mirror the effect of specific interaction sites in FGF2 for FGFR. Thus, canofins are valuable pharmacological tools to study the functional roles of specific molecular interactions of FGF2 with FGFR.
Manfe V., et al. J. Neurosci, 114; 74-86 ,2010.
It has been established that the adult mouse forebrain contains multipotential (neuronal/glial) progenitor cells that can be induced to proliferate in vitro when epidermal growth factor is provided. These cells are found within the subventricular zone of the lateral ventricles, together with other progenitor cell populations, whose requirements for proliferation remain undefined. Using basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF), we have isolated multipotential progenitors from adult mouse striatum. These progenitors proliferate and can differentiate into cells displaying the antigenic properties of astrocytes, oligodendrocytes, and neurons. The neuron-like cells possess neuronal features, exhibit neuronal electrophysiological properties, and are immunoreactive for GABA, substance P, choline acetyl-transferase, and glutamate. Clonal analysis confirmed the multipotency of these bFGF-dependent cells. Most significantly, subcloning experiments demonstrated that they were capable of self-renewal, which led to a progressive increase in population size over serial passaging. These results demonstrate that bFGF is mitogenic for multipotential cells from adult mammalian forebrain that possess stem cell properties.
Gritti, et al. J. Neurosci, 16(3); 1091-100, 1996.
The defining characteristic of obesity is increased adipose tissue (AT) mass following chronic positive energy supply. AT mass is determined by adipocyte number and size, which reflect proliferation and differentiation of preadipocytes and hypertrophy of pre-existing adipocytes. The molecular pathways governing AT expansion are incompletely defined. We previously reported that FGF-1 primes proliferating primary human preadipocytes (phPA), thereby increasing adipogenesis. Here we examined whether FGF-1's adipogenic actions were due to modulation of other FGFs. Treatment of phPA with FGF-1 reduced FGF-2 mRNA/protein by 80%. To examine a putative functional role we performed siRNA knockdown studies. Following FGF-2 knockdown preadipocyte proliferation was decreased and expression of adipogenic genes (PPAR?, G3PDH and adiponectin) was increased at day 1 of differentiation. These results suggest that changes in endogenous FGF-2 levels contribute to FGF-1's early adipogenic effects and highlight the complexity of the paracrine interplay between FGFs within human AT.
Hutley LJ, et al., Mol Cell Endocrinol, 339(1-2); 165-71, 2011.
PURPOSE: Epidermal keratinocytes, which can be severely damaged after ionizing radiation (IR), are rapid turnover cells that function as a barrier, protecting the host from pathogenic invasion and fluid loss. We tested fibroblast growth factor-peptide (FGF-P), a small peptide derived from the receptor-binding domain of FGF-2, as a potential mitigator of radiation effects via proliferation and the barrier function of keratinocytes.
METHODS AND MATERIALS: Keratinocytes isolated from neonatal foreskin were grown on transwells. After being exposed to 0, 5, or 10 Gy IR, the cells were treated with a vehicle or FGF-P. The permeability of IR cells was assessed by using transepithelial electrical resistance (TEER) and a paracellular tracer flux of fluorescein isothiocyanate-conjugated bovine serum albumin (FITC-BSA) with Ussing chambers. The cell proliferation was measured with yellow tetrazolium salt (MTT) and tritiated thymidine ([3H]-TdR) assays. The phosphorylation of extracellular signal-regulated kinases (ERK) was measured in an enzyme-linked immunosorbent (ELISA)-like assay, and the proteins related to tight junctions (TJ) and adherens junctions (AJ) were examined with Western blotting. We used a mouse model to assess the ability of FGF-P to promote the healing of skin ?burns created with a strontium applicator.
RESULTS: We found (1) FGF-P reduced the permeability of irradiated keratinocytes, as evidenced by increased TEER and decreased diffusion of FITC-BSA, both associated with the regulation of different proteins and levels of TJ and AJ; and (2) FGF-P enhanced the proliferation of irradiated keratinocytes, as evidenced by increased MTT activity and [3H]-TdR incorporation, which was associated with activation of the ERK pathway; and (3) FGF-P promoted the healing of skin ?burns.
CONCLUSIONS: FGF-P enhances the barrier function, including up-regulation of TJ proteins, increases proliferation of human keratinocytes, and accelerates the healing of skin ?burns. FGF-P is a promising mitigator that improves the proliferation and barrier function of keratinocytes after IR.
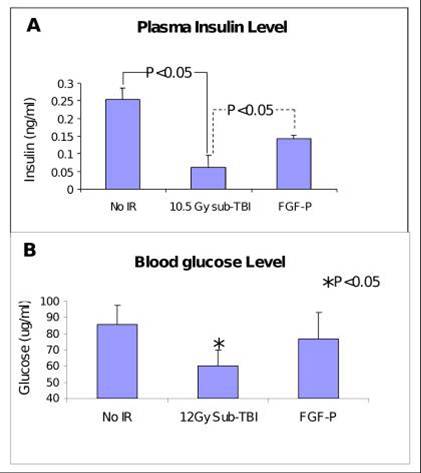
Insulin and glucose levels in plasma collected from BALB/c mice on day 3.5 after 10.5 Gy sub-TBI. Insulin and glucose were increased by FGF-P treatment (*P<0.05).
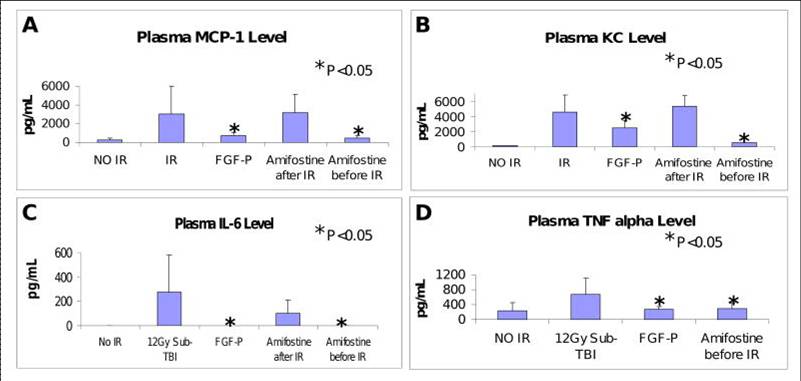
Levels of MCP-1, IL6, KC, and TNFa in plasma collected from BALB/c mice on day 3.5 after 10.5 Gy sub-TBI. These IR-induced pro-inflammatory molecules were reduced by FGF-P and Amifostine (0.5 hr pre-IR but not post-IR) (*P <0.05 )
Zhang K., et al. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys, 81(1); 248-54, 2011.
From Widberg C. H. et al. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 2009;296:E121-E131


