|
|
|
Chromogranin A & its Derived Peptides |
New Tumor Biomarker, Cardiovascular and Alzheimer-related Peptides |
Chromogranin A is the precursor to several functional peptides including vasostatin, pancreastatin, catestatin and parastatin. These peptides negatively modulate the neuroendocrine function of the releasing cell (autocrine) or nearby cells (paracrine). Other peptides derived from chromogranin A with uncertain function include chromostatin, WE-14 and GE-25.
Vasostatin
|
%053-33%;%053-35%;%053-32%
|
Pancreastatin
Pancreastatin is a 49 amino acid peptide produced by degradation of Chromo-granin A. It inhibits Chromogranin A and Parathyroid Hormone release. Pancreastatin also inhibits release of Somatostatin upon glucose stimulation. It may also control carbohydrate metabolism and hyperglycemia. Although there are no compounds with significant structural homology with Pancreastatin, there are minor similarities to Gastrin and Anti-Diuretic Hormone. Pancreastatin reduces the the early phase of Glucose induced Insulin release. Suppression of Insulin release upon Glucose stimulation is a characteristic feature of Type II Diabetes. Pancreastatin could play an important therapeutic role in the treatment of diabetes. Pancreastatin also inhibits release of Somatostatin. It may also control carbohydrate metabolism and hyperglycemia.
Catestatin
Catestatin is a 21-amino acid residue, cationic and hydrophobic peptide that is formed endogenously by proteolytic cleavage of its precursor chromogranin A, a major protein co-stored and co-released with catecholamines from the storage vesicles in adrenal chromaffin cells and adrenergic neurons. This peptide exhibits potent catecholamine release-inhibitory activity by acting on the neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptor. It also stimulates histamine release from mast cells via heterotrimeric G-proteins in a receptor-independent manner. Plasma levels of catestatin are diminished not only in hypertensive patients but also in their still-normotensive offspring, indicating its role in the pathogenesis of hypertension. Consistently, exogenous catestatin rescues hypertension in chromogranin A knockout mice and diminishes blood pressure responses to activation of sympathetic outflow in rats. These hypotensive actions of catestatin may be caused directly by autocrine inhibition of catecholamine release from the sympathoadrenal system and indirectly by paracrine stimulation of the potent vasodilator histamine release from mast cells.
|
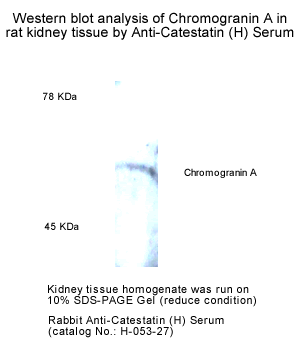
%053-27%
|
| |
|
%053-28%
|
| |
|
%053-29%
|
Other Products
|
%053-07%;%053-18%;%053-26%;%053-30%;%053-31%;%053-19%;%053-20%;%053-21%;%053-22%;%053-23%;%Serpinin%
|
|
|

|
Chromogranin A is known as an important marker of neuroendocrine tumors. In cardiovascular medicine, however, chromogranin A measurement has only recently gained interest, since increased concentrations in the circulation are associated with risk of clinical worsening and death in patients with acute coronary syndromes or chronic heart failure. In this article, we summarize the current clinical data on chromogranin A as a biomarker in cardiovascular disease from high-risk conditions; for example, obesity, hypertension and diabetes, to overt heart failure. Biological activity of the various chromogranin A fragments, including the intact precursor itself, will not be covered in the present review. Instead, we highlight the complexity of chromogranin A as a plasma marker, where the protein is extensively and variably processed to a plethora of peptide fragments. Current immunological methods for clinical measurement differ dramatically with respect to both epitope choice and clinical validation.
Goetze JP, Alehagen U, Flyvbjerg A et al., Biomark Med. 2014 Jan;8(1):133-40. doi: 10.2217/bmm.13.102.
|
|
|
|

|
Pancreastatin (PST) is a regulatory peptide containing 49 amino acids, first isolated from porcine pancreas. Intracellular and extracellular processing of the prohormone Chromogranin A (Chga) results various bioactive peptides of which PST has dysglycemic activity. PST regulates glucose, lipid, and protein metabolism in liver and adipose tissues. It also regulates the secretion of leptin and expression of leptin and uncoupling protein 2 in adipose tissue. In Chga knockout mice, PST induces gluconeogenesis in the liver. PST reduces glucose uptake in mice hepatocytes and adipocytes. In rat hepatocytes, PST induces glycogenolysis and glycolysis and inhibits glycogen synthesis. In rat adipocytes, PST inhibits lactate production and lipogenesis. These metabolic effects are confirmed in humans. In the dual signaling mechanism of PST receptor, mostly PST activates Gαq/11 protein leads to the activation of phospholipase C β3-isoform, therefore increasing cytoplasmic free calcium and stimulating protein kinase C. PST inhibits the cell growth in rat HTC hepatoma cells, mediated by nitric oxide and cyclic GMP production. Elevated levels of PST correlating with catecholamines have been found in gestational diabetes and essential hypertension. Rise in the blood PST level in Type 2 diabetes suggests that PST is a negative regulator of insulin sensitivity and glucose homeostasis.
Valicherla GR, Hossain Z, Mahata SK et al., Physiol Genomics. 2013 Nov 15;45(22):1060-71. doi: 10.1152/physiolgenomics.00131.2013. Epub 2013 Sep 24.
|
|
|
|

|
Catecholamines (CAs) and granin peptides are costored in dense-core vesicles within the chromaffin cells of the adrenal medulla and in other endocrine organs and neurons. Granins play a major functional and structural role in chromaffin cells but are ubiquitous proteins, which are present also in secretory cells of the nervous, endocrine, and immune systems, where they regulate a number of cellular functions. Furthermore, recent studies also demonstrate that granin-derived peptides can functionally interact with CA to modulate key physiological functions such as lipolysis and blood pressure. In this chapter, we will provide a brief update on the interaction between CA and granins at the cellular and organ levels. We will first discuss recent data on the regulation of exocytosis of CA and peptides from the chromaffin cells by the sympathetic nervous system with a specific reference to the prominent role played by splanchnic nerve-derived pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating peptide (PACAP). Secondly, we will discuss the role of granins in the storage and regulation of exocytosis in large dense-core vesicles. Finally, we will provide an up-to-date review of the roles played by two granin-derived peptides, the chromogranin A-derived peptide catestatin and the VGF-derived peptide TLQP-21, on lipolysis and obesity. In conclusion, the knowledge gathered from recent findings on the role played by proteins/peptides in the sympathetic/target cell synapses, discussed in this chapter, would contribute to and provide novel mechanistic support for an increased appreciation of the physiological role of CA in human pathophysiology.
Borges R, Dominguez N, Smith CB et al., Adv Pharmacol. 2013;68:93-113. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-411512-5.00005-1.
|
|
|
|

|
We used mass spectrometry-based protein identification to determine the presence of granins and other proteins in the mouse neuroblastoma secretome. We detected polypeptides derived from four members of the granin family: chromogranin A, chromogranin B, secretogranin III, and VGF. Many of them are derived from previously described biologically active regions; however, for VGF and CgB, we detected peptides not related to known bioactivities. Along with granins, we identified 115 other proteins secreted by mouse neuroblastoma cells, belonging to different functional categories. Fifty-six out of 119 detected proteins possess the signal fragments required for translocation into endoplasmic reticulum. Sequences of remaining 63 proteins were analyzed using SecretomeP algorithm to determine probability of nonclassical secretion. Identified proteins are involved in the regulation of cell cycle, proliferation, apoptosis, angiogenesis, proteolysis, and cell adhesion.
Rozek W, Kwasnik M, Debski J, et al., Tumour Biol. 2013 Jun;34(3):1773-81. doi: 10.1007/s13277-013-0716-0. Epub 2013 Mar 22.
|
|
|
|

|
INTRODUCTION:
Chromogranin A is a neuroendocrine secretory product and its loss is a feature of malignant NEN de-differentiation. We hypothesized that chromogranin A fragments were differentially expressed during NEN metastasis and played a role in the regulation of NEN proliferation.
METHODS:
Chromogranin A mRNA (PCR) and protein (ELISA/western blot) were studied in 10 normal human mucosa, 5 enterochromaffin cell preparations, 26 small intestinal NEN primaries and 9 liver metastases. Cell viability (WST-1 assay), proliferation (bromodeoxyuridine ELISA) and expression of AKT/AKT-P (CASE ELISA/western blot) in response to chromogranin A silencing, inhibition of prohormone convertase and mTOR inhibition (RAD001/AKT antisense) as well as different chromogranin A fragments were examined in 4 SI-NEN cell lines.
RESULTS:
Chromogranin A mRNA and protein levels were increased (37-340 fold, p<0.0001) in small intestinal NENs compared to normal enterochromaffin cells. Western blot identified chromogranin A-associated processing bands including vasostatin in small intestinal NENs as well as up-regulated expression of prohormone convertase in metastases. Proliferation in small intestinal NEN cell lines was decreased by silencing chromogranin A as well as by inhibition of prohormone convertase (p<0.05). This inhibition also decreased secretion of chromogranin A (p<0.05) and 5-HT (p<0.05) as well as expression of vasostatin. Metastatic small intestinal NEN cell lines were stimulated (50-80%, p<0.05) and AKT phosphorylated (Ser473: p<0.05) by vasostatin I, which was completely reversed by RAD001 (p<0.01) and AKT antisense (p<0.05) while chromostatin inhibited proliferation (~50%, p<0.05).
CONCLUSION:
Chromogranin A was differentially regulated in primary and metastatic small intestinal NENs and cell lines. Chromogranin A fragments regulated metastatic small intestinal NEN proliferation via the AKT pathway indicating that CgA plays a far more complex role in the biology of these tumors than previously considered.
Giovinazzo F, Schimmack S, Svejda B et al., PLoS One. 2013 Nov 19;8(11):e81111. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0081111.
|
|

|
Willis M at el. J Neural Transm. 2011 May;118(5):727-35. Epub 2011 Apr 30.
|
|

|
Synaptic disturbances may play a key role in the pathophysiology of
neuropsychiatric diseases. In this article, we review immunohistological
findings of chromogranin peptides in neurodegenerative and
neurodevelopmental disorders, with particular emphasis on Alzheimer's
disease, the disorder chromogranins have been studied most extensively.
Data was collected from existing and new experimental data and medline
research. This review focuses on synaptic changes elicited by
chromogranin peptides immunoreactivity in Alzheimer's disease, as well
in schizophrenia and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS). An imbalanced
availability of chromogranin peptides may be responsible for impaired
neurotransmission and a reduced functioning of dense core vesicles.
Since chromogranin A was postulated as a potent proinflammatory agent,
we focused on chromogranin A in neuroinflammation in Alzheimer's disease
and ALS. Further understanding of role and function of chromogranin
peptides in neuropathological conditions is still required.
Willis M at el. J Neural Transm. 2011 May;118(5):727-35. Epub 2011 Apr 30.
|
|

|
Koshimizu, H. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2011 May 3. [Epub ahead of print].
|
|

|
Chromogranin A (CgA) is a member of the granin family of molecules found in secretory granules of endocrine and neuro-endocrine cells. Here, we have identified a new 23-mer CgA-derived peptide secreted from pituitary AtT-20 cells, which we named pyroGlu-serpinin (pGlu-serpinin). LC-MS studies of peptides in conditioned medium of AtT-20 cells indicate that pGlu-serpinin is derived from initial processing of mouse CgA at paired basic residues, Arg461-Arg462 and Arg433-Arg434, to yield a previously described 26 amino acid peptide, serpinin. Three amino acids are then cleaved from the N terminus of serpinin, yielding a peptide with an N-terminal glutamine, which is then subsequently pyroglutaminated. Immunocytochemistry showed co-localization of pGlu-serpinin with adrenocorticotropic hormone in secretory granules of AtT-20 cells, and it was released in an activity-dependent manner. Functional studies demonstrated that pGlu-serpinin was able to prevent radical oxygen species (hydrogen peroxide)-induced cell death of AtT-20 cells and cultured rat cerebral cortical neurons at a concentration of 1 and 10 nM, respectively. These data indicate that pGlu-serpinin has anti-apoptotic effects that may be important in neuroprotection of central nervous system neurons and pituitary cells. Furthermore, pGlu-serpinin added to the media of AtT-20 cells up-regulated the transcription of the serine protease inhibitor, protease nexin-1 (PN-1) mRNA. pGlu-serpinin's ability to increase levels of PN-1, a potent inhibitor of plasmin released during inflammatory processes causing cell death, may play a role in protecting cells under adverse pathophysiological conditions.
Koshimizu, H. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2011 May 3. [Epub ahead of print].
|
|
|
|

|
Previously we demonstrated that chromogranin A (CgA) promoted secretory granule biogenesis in endocrine cells by stabilizing and preventing granule protein degradation in the Golgi, through up-regulation of expression of the protease inhibitor, protease nexin-1 (PN-1). However, the mechanism by which CgA signals the increase of PN-1 expression is unknown. Here we identified a 2.9-kDa CgA-C-terminus peptide, which we named serpinin, in conditioned media from AtT-20 cells, a corticotroph cell line, which up-regulated PN-1 mRNA expression. Serpinin was secreted from AtT-20 cells upon high potassium stimulation and increased PN-1 mRNA transcription in these cells, in an actinomycin D-inhibitable manner. CgA itself and other CgA-derived peptides, when added to AtT-20 cell media, had no effect on PN-1 expression. Treatment of AtT-20 cells with 10 nm serpinin elevated cAMP levels and PN-1 mRNA expression, and this effect was inhibited by a protein kinase A inhibitor, 6-22 amide. Serpinin and a cAMP analog, 8-bromo-cAMP, promoted the translocation of the transcription factor Sp1 into the nucleus, which is known to drive PN-1 expression. Additionally, an Sp1 inhibitor, mithramycin A inhibited the serpinin-induced PN-1 mRNA up-regulation. Furthermore, a luciferase reporter assay demonstrated serpinin-induced up-regulation of PN-1 promoter activity in an Sp1-dependent manner. When added to CgB-transfected 6T3 cells, a mutant AtT20 cell line, serpinin induced granule biogenesis as evidenced by the presence of CgB puncta accumulation in the processes and tips. Our findings taken together show that serpinin, a novel CgA-derived peptide, is secreted upon stimulation of corticotrophs and plays an important autocrine role in up-regulating PN-1-dependent granule biogenesis via a cAMP-protein kinase A-Sp1 pathway to replenish released granules.
Koshimizu H, Mol Endocrinol. 2011 Mar 24. [Epub ahead of print]
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
Catestatin is a bioactive peptide of chromogranin A (CHGA) that is co-released with catecholamines from secretory vesicles. Catestatin may function as a vasodilator and is diminished in hypertension. To evaluate this potential vasodilator in vivo without systemic counterregulation, we infused catestatin to target concentrations of approximately 50, approximately 500, approximately 5000 nM into dorsal hand veins of 18 normotensive men and women, after pharmacologic venoconstriction with phenylephrine. Pancreastatin, another CHGA peptide, was infused as a negative control. After preconstriction to approximately 69%, increasing concentrations of catestatin resulted in dose-dependent vasodilation (P = 0.019), in female subjects (to approximately 44%) predominantly. The EC(50) (approximately 30 nM) for vasodilation induced by catestatin was the same order of magnitude to circulating endogenous catestatin (4.4 nM). No vasodilation occurred during the control infusion with pancreastatin. Plasma CHGA, catestatin, and CHGA-to-catestatin processing were then determined in 622 healthy subjects without hypertension. Female subjects had higher plasma catestatin levels than males (P = 0.001), yet lower CHGA precursor concentrations (P = 0.006), reflecting increased processing of CHGA-to-catestatin (P < 0.001). Our results demonstrate that catestatin dilates human blood vessels in vivo, especially in females. Catestatin may contribute to sex differences in endogenous vascular tone, thereby influencing the complex predisposition to hypertension.
Fung MM, Salem RM, Mehtani P et al., Clin Exp Hypertens. 2010;32(5):278-87. doi: 10.3109/10641960903265246.
|
|

|
Koshimizu, H. Regul Pept. 2010 Feb 25;160(1-3):153-9. Epub 2009 Dec 16.
|

|
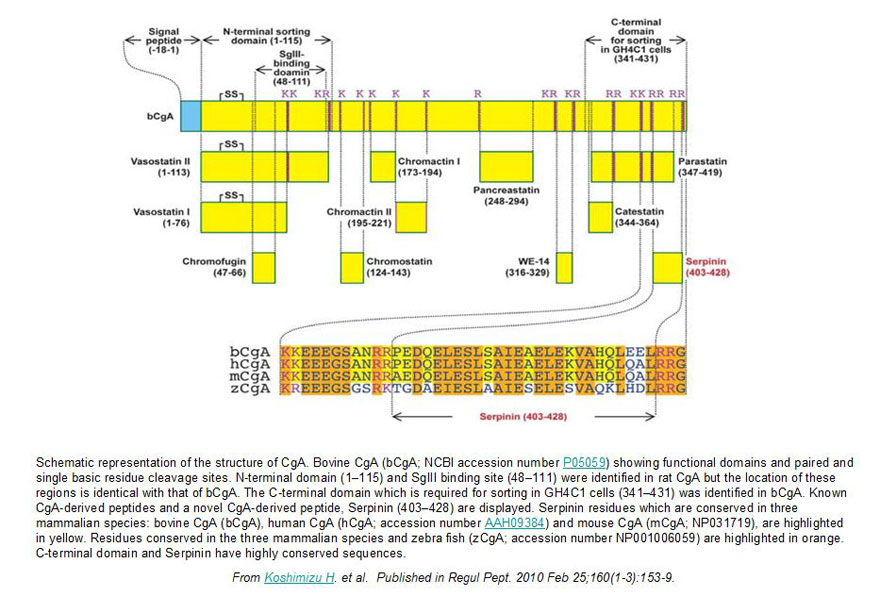
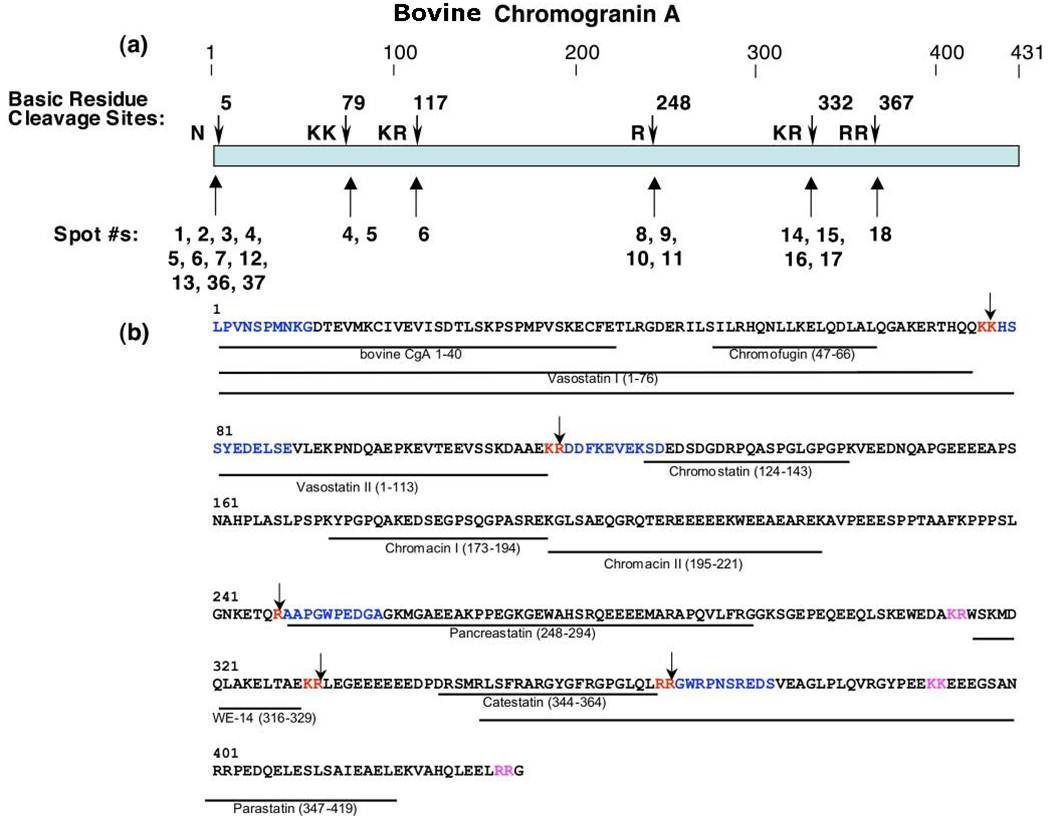
Chromogranin A (CgA), a member of the granin family serves several important cell biological roles in (neuro)endocrine cells which are summarized in this review. CgA is a "prohormone" that is synthesized at the rough endoplasmic reticulum and transported into the cisternae of this organelle via its signal peptide. It is then trafficked to the Golgi complex and then to the trans-Golgi network (TGN) where CgA aggregates at low pH in the presence of calcium. The CgA aggregates provide the physical driving force to induce budding of the TGN membrane resulting in dense core granule (DCG) formation. Within the granule, a small amount of the CgA is processed to bioactive peptides, including a predicted C-terminal peptide, serpinin. Upon stimulation, DCGs undergo exocytosis and CgA and its derived peptides are released. Serpinin, acting extracellularly is able to signal the increase in transcription of a serine protease inhibitor, protease nexin-1 (PN-1) that protects DCG proteins against degradation in the Golgi complex, which then enhances DCG biogenesis to replenish those that were released. Thus CgA and its derived peptide, serpinin, plays a significant role in granule formation and regulation of granule biogenesis, respectively, in (neuro) endocrine cells.
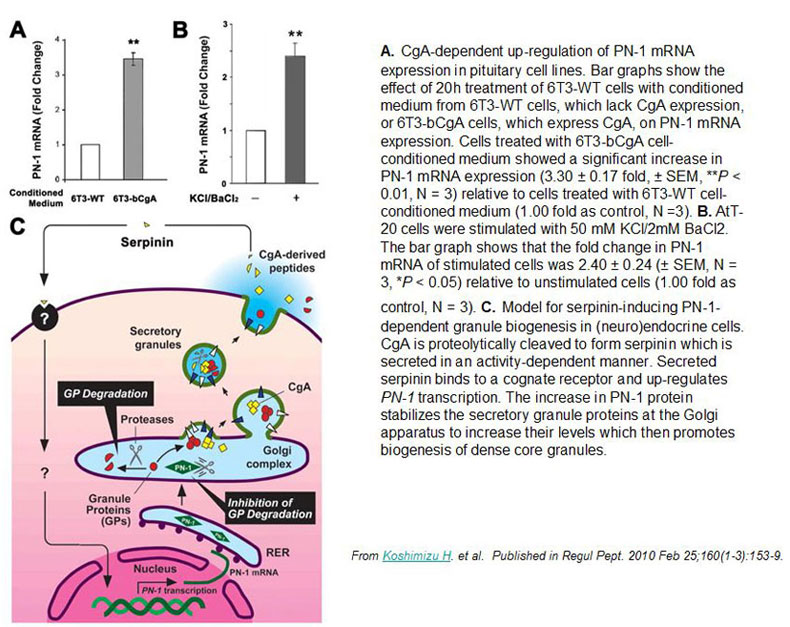
Koshimizu, H. Regul Pept. 2010 Feb 25;160(1-3):153-9. Epub 2009 Dec 16.
|
|
|
|

|
Chromogranin A (CHGA/Chga), a proprotein, widely distributed in endocrine and neuroendocrine tissues (not expressed in muscle, liver, and adipose tissues), generates at least four bioactive peptides. One of those peptides, pancreastatin (PST), has been reported to interfere with insulin action. We generated a Chga knock-out (KO) mouse by the targeted deletion of the Chga gene in neuroendocrine tissues. KO mice displayed hypertension, higher plasma catecholamine, and adipokine levels and lower IL-6 and lipid levels compared with wild type mice. Liver glycogen content was elevated, but the nitric oxide (NO) level was diminished. Glucose, insulin, and pyruvate tolerance tests and hyperinsulinemic-euglycemic clamp studies established increased insulin sensitivity in liver but decreased glucose disposal in muscle. Despite higher catecholamine and ketone body levels and muscle insulin resistance, KO mice maintained euglycemia due to increased liver insulin sensitivity. Suppressed mRNA abundance of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase and glucose-6-phosphatase (G6Pase) in KO mice further support this conclusion. PST administration in KO mice stimulated phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase and G6Pase mRNA abundance and raised the blood glucose level. In liver cells transfected with G6Pase promoter, PST caused transcriptional activation in a protein kinase C (PKC)- and NO synthase-dependent manner. Thus, PST action may be mediated by suppressing IRS1/2-phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-Akt-FOXO-1 signaling and insulin-induced maturation of SREBP1c by PKC and a high level of NO. The combined effects of conventional PKC and endothelial NO synthase activation by PST can suppress insulin signaling. The rise in blood PST level with age and in diabetes suggests that PST is a negative regulator of insulin sensitivity and glucose homeostasis.
Gayen JR, Saberi M, Schenk S et al., J Biol Chem. 2009 Oct 16;284(42):28498-509. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.020636. Epub 2009 Aug 25.
|
|

|
Arch Gerontol Geriatr. 2008 Mar 6 [Epub ahead of print]
|

|
The neuroendocrine differentiation in PC could potentially represent a
new finding with diagnostic, prognostic and therapeutic implications. This
study aimed at evaluating the clinical usefulness of CgA as a
neuroendocrine (NE) serum-marker. We investigated the role of the serum
concentration of CgA in a
study group of patients with PC. CgA was
significantly higher in the patients affected by PC as compared with the
group of healthy subjects (HS) and those with chronic pancreatitis (CHP)
(p<0.001). Also the HS group differed significantly from the CHP
control group in the serum CgA levels (p<0.001). The serum carbohydrate
antigen (CA19-9) level displayed a significant difference (p<0.001)
between the PC and the HS group. The PC and CHP groups, as well as
the HS and CHP groups showed also significant differences in the CA19-9
levels (p<0.001). One can conclude that the patients with higher CgA
levels had poorer prognosis and survival, as compared to those with lower
CgA levels. These results support the notion that the determination of
serum CgA level before treatment may be a potential prognostic factor for
PC.
Arch Gerontol Geriatr. 2008 Mar 6 [Epub ahead of print]
|
|

|
J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2008 Jan;93(1):91-5. Epub 2007 Oct 16
|

|
CONTEXT: The initial diagnosis of pheochromocytoma relies
on plasma fractionated metanephrines levels. Normal levels exclude
pheochromocytoma, but positive tests have a low positive predictive value
due to the disease's rarity.
OBJECTIVES: The objective of the study was to
evaluate three approaches to distinguish between true-positive and
false-positive tests: 1) increased cutoff for plasma fractionated
metanephrines, 2) measurement of serum/plasma chromogranin A (CGA), and 3)
urine fractionated metanephrine testing.
DESIGN: We studied
retrospectively all Mayo Clinic patients with positive plasma fractionated
metanephrine tests over a 15-month period and determined their final
diagnosis based on histology, imaging, additional biochemical tests, and
more than 1 yr follow-up. For a subgroup, urine fractionated metanephrine
results were available. All original plasma samples were retested for CGA.
RESULTS: Of 140 patients, 40 had a chromaffin tumor confirmed and 100
excluded, indicating a positive predictive value of plasma fractionated
metanephrines of 28.6%. Increasing the threshold for a positive test
improved specificity to 98% but missed eight cases (20%). Incorporation of
urine fractionated metanephrine testing as follow-up test achieved 80%
specificity and 91% sensitivity. The corresponding figures for CGA were 71
and 87% for all patients and 89 and 87% when patients taking proton pump
inhibitors were excluded.
CONCLUSIONS: Unless plasma fractionated
metanephrines levels are elevated more than 4-fold above the upper limit
of normal, patients with a positive plasma fractionated metanephrines test
should be evaluated with urine fractionated metanephrines and serum/plasma
CGA assays before being subjected to imaging or invasive diagnostic
tests.
J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2008 Jan;93(1):91-5. Epub 2007 Oct 16
|
|

|
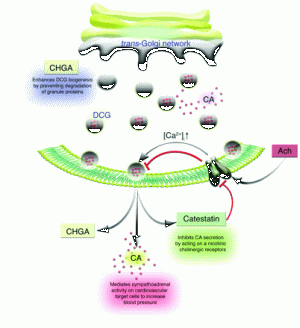 |
Relationship of CHGA-mediated dense-core secretory granule (DCG) biogenesis, catecholamine (CA) secretion, and its subsequent inhibition by
the CHGA-derived peptide catestatin in the maintenance of blood pressure by the adrenal gland. CHGA, as a full-length molecule, initiates
dense-core secretory granule biogenesis at the trans-Golgi network of adrenal chromaffin cells. Current data suggests that CHGA
enhances granule biogenesis by preventing posttranslational degradation of other granule proteins in the Golgi complex. In the cytoplasm,
catecholamine is synthesized and transported into the dense-core secretory granules via vesicular monoamine transporters. Upon stimulation by
acetylcholine (Ach), catecholamine is coreleased with CHGA and catestatin from the granules. Secreted catecholamine triggers cardiovascular target
cells to augment blood flow. This sympathoadrenal activity is then antagonized by the action of catestatin on cholinergic receptors to
inhibit catecholamine secretion. [Ca2+]i, intracellular calcium concentration.
Kim et al. J. Clin. Invest. 115:1711-1713 (2005)
|
|
|

|
Imbrogno S, et al. Gen Comp Endocrinol. 2004 Oct;139(1):20-8
|

|
We have studied the effects of exogenous human recombinant
Vasostatin-1 (VS-1), Vasostatin-2 (VS-2) and the human Chromogranin A
(CGA) 7-57 synthetic peptides on the mechanical performance of the
isolated and perfused working eel (Anguilla anguilla) heart. Under basal
conditions, the three peptides decreased stroke volume (SV) and stroke
work (SW), thus exerting negative inotropism. The VS-1-mediated negative
inotropism was abolished by exposure to inhibitors of either Gi/o protein
(pertussis toxin; PTx) or M1 muscarinic receptors (Pirenzepine) or calcium
(Lantanum and Diltiazem) and potassium (Ba2+, 4-aminopyridine,
tetraethylammonium, glibenclamide) channels, while it required an intact
endocardial endothelium (EE). Using NG-monomethyl-L-arginine (L-NMMA) as
an inhibitor of nitric oxide (NO) synthase (NOS), and hemoglobin as a NO
scavenger, we demonstrated the obligatory role of NO signaling in
mediating the vasostatin response. Pretreatment with either a specific
inhibitor of soluble guanylate cyclase (GC)
1H-(1,2,4)oxadiazolo-(4,3-a)quinoxalin-1-one (ODQ), or the inhibitor of
the cGMP-activated protein kinase (PKG) KT5823, abolished the
VS-1-mediated inotropism, indicating the cGMP-PKG component as a crucial
target of NO signaling. Of note, VS-1 was effective in counteracting the
adrenergic (Isoproterenol and Phenylephrine)-mediated positive inotropism.
These findings provide the first evidence that vasostatins exert
cardiotropic action in fish, thus suggesting their long evolutionary
history as well as their species-specific mechanisms of
action.
Imbrogno S, et al. Gen Comp Endocrinol. 2004 Oct;139(1):20-8
|
|
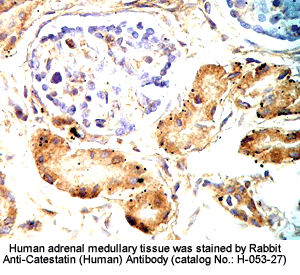 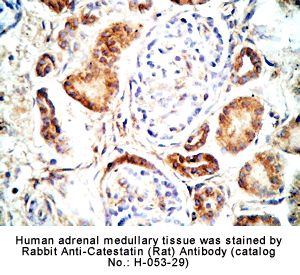
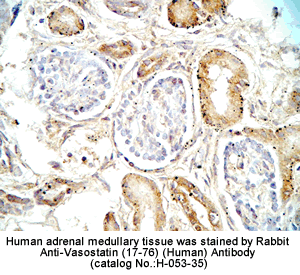
Tissue Sample |
Human adrenal medullary |
Fixative |
10% formalin |
Embedding |
Paraffin |
Negative Control |
No primary antibody |
Pretreatment |
N/A |
Blocking |
3% H2O2, 2% Normal Goat Serum |
Primary Antibody |
Rabbit anti-Catestatin (Human) Antibody (Cat. No.:
H-053-27) |
Optimal Dilution |
1: 500 |
Secondary Antibody |
Goat Anti-Rabbit IgG, Biotinylated (1:400), 30 min |
Amplification |
Streptavidin-HRP (Vector), 1:400, 30 min |
Detection System |
HRP |
Substrate |
DAB (Sigma), 3 min |
Counterstained |
Hematoxylin, 30 sec |
Tissue Sample |
Human adrenal medullary tissues |
Fixative |
10% formalin |
Embedding |
Paraffin |
Negative Control |
No primary antibody |
Pretreatment |
N/A |
Blocking |
3% H2O2, 2% Normal Goat Serum |
Primary Antibody |
Rabbit Anti-Catestatin (Rat) Antibody (Cat. No.: H-053-29) |
Optimal Dilution |
1: 500 |
Secondary Antibody |
Goat Anti-Rabbit IgG, Biotinylated (1:400), 30 min |
Amplification |
Streptavidin-HRP (Vector), 1:400, 30 min |
Detection System |
HRP |
Substrate |
DAB (Sigma), 3 min |
Counterstained |
Hematoxylin, 30 sec |
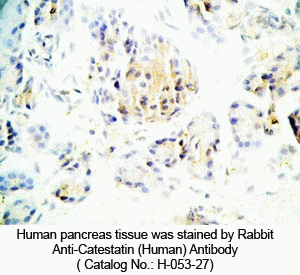 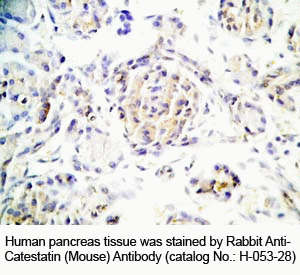
Tissue Sample |
Human pancreas tissues |
Fixative |
10% formalin |
Embedding |
Paraffin |
Negative Control |
No primary antibody |
Pretreatment |
N/A |
Blocking |
3% H2O2, 2% Normal Goat Serum |
Primary Antibody |
Rabbit Anti-Catestatin (Mouse) Antibody (Cat. No.: H-053-28) |
Optimal Dilution |
1: 500 |
Secondary Antibody |
Goat Anti-Rabbit IgG, Biotinylated (1:400), 30 min |
Amplification |
Streptavidin-HRP (Vector), 1:400, 30 min |
Detection System |
HRP |
Substrate |
DAB (Sigma), 3 min |
Counterstained |
Hematoxylin, 30 sec |
Tissue Sample |
Human pancreas tissues |
Fixative |
10% formalin |
Embedding |
Paraffin |
Negative Control |
No primary antibody |
Pretreatment |
N/A |
Blocking |
3% H2O2, 2% Normal Goat Serum |
Primary Antibody |
Rabbit anti-Catestatin (Human) Antibody (Cat. No.: H-053-27) |
Optimal Dilution |
1: 500 |
Secondary Antibody |
Goat Anti-Rabbit IgG, Biotinylated (1:400), 30 min |
Amplification |
Streptavidin-HRP (Vector), 1:400, 30 min |
Detection System |
HRP |
Substrate |
DAB (Sigma), 3 min |
Counterstained |
Hematoxylin, 30 sec |
Tips: See More Research Abstracts, Antibody Stainings, Immunoassay Kits Curves and Sequences by clicking the tabs on the top.
|
|
|
%alzheimer%;serpinin;manserin
|
|
|


