| Image | 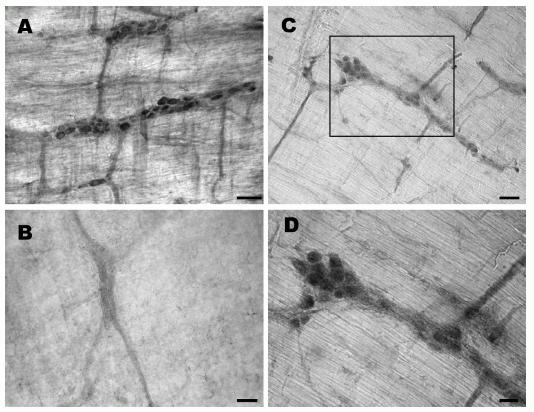
Obestatin- and preproghrelin-immunoreactive cells in the rat myenteric plexus. (A) Several myenteric ganglia contain clusters of obestatin-immunoreactive cells. (B) Immunoreactivity is not detected in myenteric plexus processed with obestatin antiserum pre-absorbed with the peptide (1 mg/ml) overnight. (C) Several myenteric ganglia contain preproghrelin-immunoreactive cells of varying intensities. (D) A higher magnification of the area shown in C, where several preproghrelin-immunoreactive ganglion cells are clearly seen. Scale bar: A-C, 50 mm and D, 25 mm. Dun et al. J Endocrinol. 2006 Nov;191(2):481-9.
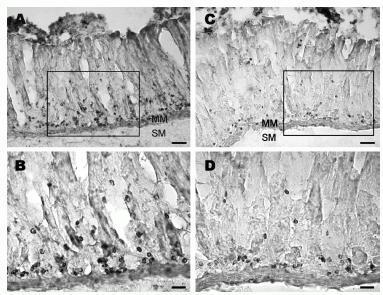
Longitudinal strips of rat stomach labeled with obestatin- or preproghrelin antiserum. (A) Obestatin-immunoreactive cells occur mostly in the glands of gastric mucosa. (B) A higher magnification of the area in A where strongly labeled cells are seen in the glandular base. (C) Preproghrelin-immunoreactive cells are localized near the base of the glands. (D) A higher magnification showing immunoreactive cells localized mainly to the glandular base. MM, muscularis mucosae and SM, submucosa. Scale bar: A and C, 100 mm; B and D, 25 mm. Dun et al. J Endocrinol. 2006 Nov;191(2):481-9. Immunohistochemical procedures Animals were anesthetized with urethane (1.2 g/kg, i.p.) and intracardially perfused with 0.1 M PBS followed by freshly prepared 4% paraformaldehyde/0.2% picric acid in PBS. A segment of stomach, small and large intestine were removed, postfixed for 2 h, and stored in 30% sucrose/PBS solution overnight. In preparing the myenteric plexus, layers of smooth muscles were scraped as much as possible by cotton swabs and the plexus was processed as a whole mount (Dun et al. 1997). In single staining, tissues were processed for irOBS by the avidin-biotin complex procedure (Brailoiu et al. 2005a,b). Tissues were first treated with 3% H2O2 to quench endogenous peroxidase, washed several times and blocked with 10% normal goat serum. Tissues were then incubated in obestatin- or preproghrelin antiserum for 48 h at 4 8C with gentle agitation. Obestatin antiserum, a rabbit polyclonal directed against the rat/mouse obestatin (catalog No.: H-031-90) (FNAPFDVGIKLSGAQYQQHGRAL-NH2; Phoenix Pharmaceuticals, Inc., Belmont, CA, USA), was used at a dilution of 1:1000 with 0.4% Triton X-100 and 1% BSA in PBS. Rabbits were immunized with obestatin conjugated to Q3 thyroglobulin by the N-ethyl-N0-(3-dimethylaminopropyl) carbodiimide method. Preproghrelin antiserum, a rabbit polyclonal directed against the human preproghrelin (86-117) (Catalog No.:H-031-36) LSGVQYQQHSQALGKFLQDILWEEAKEAPADK; Phoenix Pharmaceuticals, Inc.), was used at a dilution of 1:750-1000. After thorough rinsing, sections were incubated in biotinylated anti-rabbit IgG (1:150 dilution, Vector Laboratories, Burlingame, CA, USA) for 2 h. Sections were rinsed with PBS and incubated in avidin-biotin complex solution for 1 h (1:100 dilution, Vector Laboratories). Following several washes in Tris-buffered saline, sections were incubated in 0.05% diaminobenzidine/0.001% H2O2 solution and washed for at least 2 h with Tris-buffered saline. Sections were mounted on slides with 0.25% gel alcohol, air-dried, dehydrated with absolute alcohol followed by xylene, and coverslipped with Permount. To establish the specificity of obestatin- or preproghrelin antiserum, myenteric sections were processed with obestatin- or preproghrelin antiserum pre-absorbed with the rat/ mouse obestatin peptide or preproghrelin (86-117; 1 mg/ml) overnight. In the case of double-labeling experiments, tissue sections were first blocked with normal goat serum (1:10 in PBS, 0.5% BSA, 0.4% Triton X-100) and then incubated in obestatin antiserum (1:750 dilution) for 48 h in a cold room, with gentle agitation. Following several washes with PBS, sections were incubated with biotinylated anti-rabbit IgG (1:50, Vector Laboratories) for 2 h. After several washes with PBS, tissues were incubated with Avidin Texas Red for 3 h. After rinsing with PBS for 1 h, tissues were blocked with normal donkey serum, and incubated with choline acetyltransferase (ChAT) antiserum (1:1000; a guinea pig polyclonal from Bachem Bio Sciences, Inc., King of Prussia, PA, USA) for 48 h in a cold room. After washing with PBS for 30 min, tissues were incubated in fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC)- conjugated Affini Pure donkey anti-guinea pig IgG (1:50, Q4 Jackson Laboratories) for 3 h. Sections were washed for 1 h with PBS, mounted in Citifluor and coverslipped. Sections were examined under a confocal scanning laser microscope (Leica TCS SL) with excitation/emission wavelengths set to 488 nm/520 nm for FITC and 543 nm/620 nm for Texas Red in the sequential mode.Dun et al. J Endocrinol. 2006 Nov;191(2):481-9. 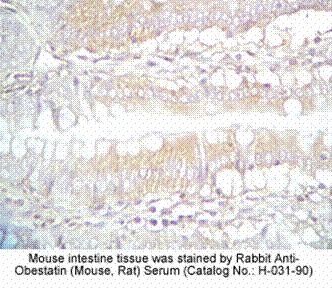
| Protocol for Immunohistochemistry: | | Tissue Sample | mouse intestine, stomach tissue | | Fixative | 10% Formalin | | Embedding | Paraffin | | Negative control | Pre-immuno serum | | Pretreatment | Intact | | Blocking | 2% Normal Goat Serum | | Primary Antibody | Rabbit Anti-Obestatin (Mouse, Rat) Serum (Catalog No.:H-031-90) | | Optimal Dilution | 1:250~500 (1hour at RT) | | Secondary Antibody | Goat anti-Rabbit IgG, Biotinylated (1:400, 30 min) | | Amplification | ABC (Vector) (1:400, 30 min) | | Detection System | HRP | | Substrate | DAB (Sigma), 3 min | | Counterstained | Hematoxylin, 30 Sec |
|


