| Image | 
Sequence information of Sef. A, nucleotide and deduced amino acid sequence of interleukin-17 receptor-like molecule (hSef). Nested RACE-PCR was used to clone the 5'-fragment of the Sef cDNA, and then the full-length cDNA was assembled by reverse transcriptase-PCR. Translated and untranslated regions of the cDNA are in uppercase and lowercase letters, respectively. Eight conserved Cys residues in the extracellular domain of the gene are in the bold boxes. The predicted signal peptide and transmembrane domain are underlined and doubly underlined, respectively. Putative TIR domain (Toll/IL-1 Receptor domain) in the intracellular domain of the gene (V358-K424) is shown in italics. Nine potential N-linked glycosylation sites are boxed. B, sequence alignment of Sef alternative splicing forms. Both splicing forms of hSef were aligned using ClustalW multiple alignment. hSef-S is shown as a truncated form, which lacks 144 amino acids at the N terminus compared with hSef. C, genomic structure of human Sef. Schematic representation of exons is marked, and spans nucleotides 427,937-498,840 (hSef) and 420,648-506,133 (hSef-S) in NT_005787.8 from human chromosome 3p21 [PDB] . The hSef (long form) has 13 exons and hSef-S (short form) has 14 exons. The start and stop codons are indicated. Xiong S, et al. hSef inhibits PC-12 cell differentiation by interfering with Ras-mitogen-activated protein kinase MAPK signaling. J Biol Chem. 2003 Dec 12;278(50):50273-82 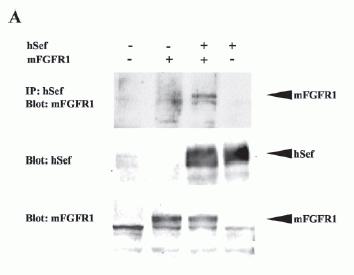
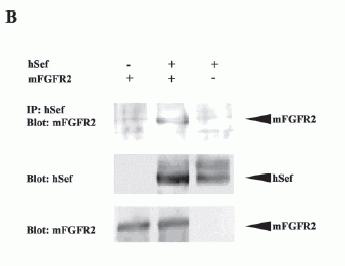

Interaction of hSef with mFGFR.
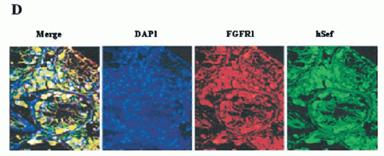
A, co-immunoprecipitation of hSef and mFGFR1. COS-7 cells were transiently transfected with mFGFR1 and hSef constructs as indicated. Whole-cell lysates were immunoprecipitated (IP) with hSef rabbit anti-serum. After electrophoresis, blots were probed with rabbit polyclonal antibody to mFGFR1(Flg). The expressions of mFGFR1 and hSef were detected by rabbit polyclonal antibody to mFGFR1 and rabbit polyclonal antibody to hSef using the whole transfected cell lysates. B, co-immunoprecipitation of hSef and mFGFR2. COS-7 cells were transiently transfected with mFGFR2 and hSef constructs as indicated. The procedure was the same as in A. C, co-localization of hSef with mFGFR2 in transfected COS-7 cells. COS-7 cells were cotransfected with mFGFR2 and hSef constructs using Effectine transfection reagent (Qiagen). hSef and mFGFR2 were stained with secondary antibodies conjugated with fluorescein isothiocyanate (green) and Cy3 (red), respectively. The co-localization of the two proteins is shown as a merged figure. D, endogenous colocalization of Sef with FGFR1 in some tissues. A triple immunofluorescence staining and confocal analyses for the endogenous colocalization of Sef with FGFR1 in normal human testis was performed according to the manufacturer's instructions. Sef staining was performed using rabbit polyclonal anti-Sef antibody followed by fluorescein isothiocyanate-labeled goat anti-rabbit IgG. FGFR1 staining was performed using mouse anti-FGFR1 antibody followed by Texas-Red-labeled goat anti-mouse IgG. Nuclear staining was performed using DAP1. One obvious co-localization of Sef and FGFR1 in testis was observed.
Western Blotting and Immunoprecipitation:
The cells were lysed in lysis buffer containing 50 mM Tris, pH 7.6, 150 mM NaCl, 1% Nonidet P-40, and 1 mM sodium orthovanadate in the presence of protease inhibitors. The immune complexes were captured with protein A or G-Sepharose, washed in lysis buffer, and resolved by SDS-PAGE. The proteins were transferred onto nitrocellulose membrane, and the membrane was blocked with 5% non-fat milk in TBST containing 0.1% Tween 20 overnight at 4 °C. Then, the indicated primary antibody Anti-h Sef Serum (1:500-2000) was incubated, followed by horseradish-peroxidase-conjugated rabbit antisheep or anti mouse antibodies as secondary antibodies and detected by chemiluminescence according to manufacturer's instructions (ECL; Amersham Biosciences).
Xiong et al. J Biol Chem. 2003 Dec 12;278(50):50273-82.
|


