Human
Opiorphin
a natural
antinociceptive modulator of opioid-dependent
pathways
Mammalian zinc ectopeptidases play important roles in turning
off neural and hormonal peptide signals at the cell surface, notably those
processing sensory information. We report here the discovery of a previously
uncharacterized physiological inhibitor of enkephalin-inactivating zinc
ectopeptidases in humans, which we have named Opiorphin. It is a QRFSR peptide
that inhibits two enkephalin-catabolizing ectoenzymes, human neutral
ecto-endopeptidase, hNEP (EC 3.4.24.11), and human ecto-aminopeptidase, hAP-N
(EC 3.4.11.2). Opiorphin displays potent analgesic activity in chemical and
mechanical pain models by activating endogenous opioid-dependent transmission.
Its function is closely related to the rat sialorphin peptide, which is an
inhibitor of pain perception and acts by potentiating endogenous mu- and
delta-opioid receptor-dependent enkephalinergic pathways. Here we demonstrate
the functional specificity in vivo of human Opiorphin. The pain-suppressive
potency of Opiorphin is as effective as morphine in the behavioral rat model of
acute mechanical pain, the pin-pain test. Thus, our discovery of Opiorphin is
extremely exciting from a physiological point of view in the context of
endogenous opioidergic pathways, notably in modulating mood-related states and
pain sensation. Furthermore, because of its in vivo properties, Opiorphin may
have therapeutic implications.
Wisner A, et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006 Nov
21;103(47):17979-84. Epub 2006 Nov 13
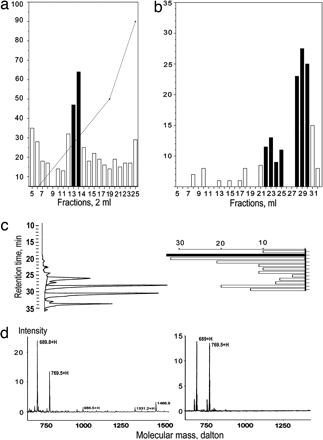
Human Opiorphin
identified in salivary secretions. (a–c) Percentage inhibition of SP breakdown
by human cell-surface endopeptidases. Salivary fractions were analyzed for their
potency to inhibit the endoproteolysis of the NEP-sensitive natural substrate,
SP, by human cells expressing membraneanchored hNEP (bars). (a) CE-HPLC profile
of salivary methanol acid extracts obtained from 45 ml of human saliva. The
dotted line represents the percentage of ammonium acetate buffer (1 M). (b)
RP-HPLC profile of the major CE-HPLC active fractions (black bars in a). (c)
Final RP-HPLC elution profile of
the major RP-HPLC active fractions (black
bars in b) and for their absorbance at 264 nm (black line). (d Left) SELDI-TOF
MS analysis of the major RP-HPLC active fraction of the last purification step
(black bar in c Right). (d Right) SELDI-TOF MS analysis of the reference
synthetic QRFSR peptide. Wisner A, et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006 Nov
21;103(47):17979-84. Epub 2006 Nov 13
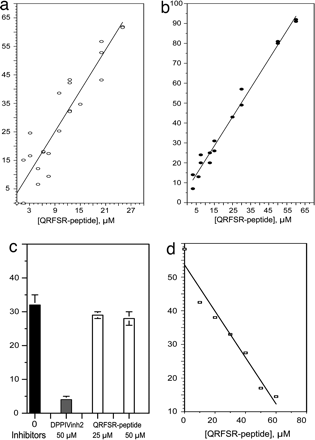
Human Opiorphin demonstrates functional activity in vitro. (a)
Concentration-dependent inhibition by OpiorphinQRFSRpeptide of SP
endoproteolysis, mediated by hNEP expressed at the surface of LNCaP cells. Each
point (white circle) representsthepercentageof intact
3H-SPrecovered(percentageof velocity without inhibitor velocity in presence of
inhibitorvelocity without inhibitor), which was measured in the absence or in
the presence of various concentrations of QRFSR peptide (in mM). (b) Specific concentration-dependent inhibition by
Opiorphin QRFSR peptide of SP endoproteolysis by pure recombinant hNEP. Each
point (black circle) representsthepercentageof intact 3H-SPrecovered(measured
and calculated as in a). (c) The breakdown of SP by recombinant hDPPIV in the
absence (black bar) or in the presence (white bars) of Opiorphin QRFSR peptide
or in the presence of synthetic DPPIV-inh2 (gray bar). The values represent the
mean +- SD (n = 3) of the percentage of specific 3H-SP hydrolysis by hDPPIV. (d)
Specific concentration-dependent inhibition by Opiorphin QRFSR peptide of
Met-enkephalin cleavage by purified soluble pAP-M. Each point (white square)
represents (mean of two independent experiments) the percentage of Metenkephalin
hydrolysis by pAP-M analyzed in the absence or in the presence of various
concentrations of QRFSR peptide (in M) by RP-HPLC. Wisner A, et al. Proc Natl
Acad Sci U S A. 2006 Nov 21;103(47):17979-84. Epub 2006 Nov 13
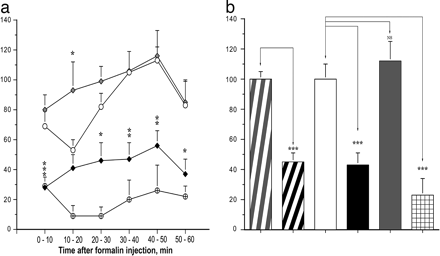
Opiorphin-derived
peptide displays potent analgesic activity in vivo in rat pain model. (a–b)
Evaluation of the pain response of rats to noxious chemical stimuli after
administration of the Opiorphin-derived peptide YQRFSR. (a) Effects of YQRFSR
peptide (black diamond; 1 mgkg) compared with morphine (crossed circle; 3mgkg
i.p. given 15 min before test) and vehicle (white circle) in the absence or
presence of the opioid
antagonist naloxone (gray diamond; 3 mg/kg s.c. given
30 min before test) on the number of body tremors during the six 10-min periods
of the formalin test. (b) Pain index calculated from results shown in a by the
AUCI method described in Materials and Methods. The values represent the mean +-
SEM of eight animals for each condition: pain index based on paw licking
duration (gray-striped bar, vehicle; black-striped bar,
YQRFSR peptide); pain
index based on body tremor number (white bar, vehicle; black bar, YQRFSR
peptide; gray bar, YQRFSR peptide plus
naloxone; hatched bar,
morphine). *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***; P
< 0.001 by Dunnett’s t test. Wisner A, et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006
Nov 21;103(47):17979-84. Epub 2006 Nov 13


