Adiponectin
Receptor-1 &-2 (AdipoR1 & AdipoR2)
two recently identified receptors
 More
Info on Adiponectin, Adiponectin Receptors and Adiponectin
EIA Kits More
Info on Adiponectin, Adiponectin Receptors and Adiponectin
EIA Kits
 Adiponectin
related products Adiponectin
related products
|
| 
|
|
|
|
|
| |
| Two
Antibodies for Adiponectin Receptor 1 & 2 Western Blot
Analysis |
|
|
| 
|
|
|
Adiponectin Receptor-1 in rat heart tissue was detected by
Anti-Adiponectin Receptor-1 (41-65) (Human) Serum
(Catalog No.: H-001-45) (1:500)
|
| |
| 
|
Adiponectin Receptor-1 in rat heart tissue was detected by
Anti-Adiponectin Receptor-1 (357-375) (Human) Serum
(Catalog No.: H-001-44) (1:200)
|
|
Antibody for Adiponectin Receptor 1 Immunohistochemistry
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
| 
|
|
| 
|
|
|

|
|
| |
New Antibody for Adiponectin
Receptor 2 Immunohistochemistry |

|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
|

|
|
| 
|
|
| 
|
| |
|
 Adiponectin
related products Adiponectin
related products
|
| |
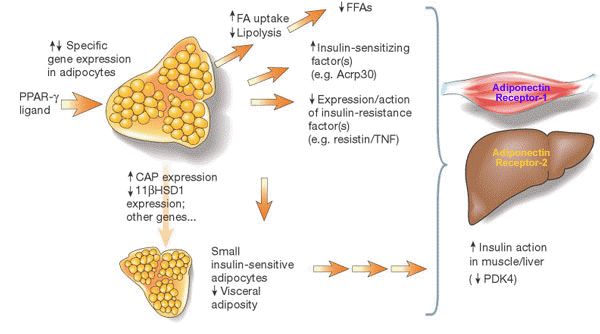
Cloning of adiponectin
receptors that mediate antidiabetic metabolic effects |
Adiponectin
(also known as 30-kDa adipocyte complement-related protein;
Acrp30) is a hormone secreted by adipocytes that acts as an
antidiabetic and anti-atherogenic adipokine. Levels of adiponectin
in the blood are decreased under conditions of obesity, insulin
resistance and type 2 diabetes. Administration of adiponectin
causes glucose-lowering effects and ameliorates insulin resistance
in mice. Conversely, adiponectin-deficient mice exhibit insulin
resistance and diabetes. This insulin-sensitizing effect of
adiponectin seems to be mediated by an increase in fatty-acid
oxidation through activation of AMP kinase and PPAR-alpha.
Here we report the cloning of complementary DNAs encoding
adiponectin receptors 1 and 2 (AdipoR1 and AdipoR2) by expression
cloning. AdipoR1 is abundantly expressed in skeletal muscle,
whereas AdipoR2 is predominantly expressed in the liver. These
two adiponectin receptors are predicted to contain seven transmembrane
domains, but to be structurally and functionally distinct
from G-protein-coupled receptors. Expression of AdipoR1/R2
or suppression of AdipoR1/R2 expression by small-interfering
RNA supports our conclusion that they serve as receptors for
globular and full-length adiponectin, and that they mediate
increased AMP kinase and PPAR-alpha ligand activities, as
well as fatty-acid oxidation and glucose uptake by adiponectin. |
Yamauchi
T, et al. Nature. 2003 Jun 12;423(6941):762-9 |
| |
| Expression
of adiponectin receptors in human macrophages and regulation
by agonists of the nuclear receptors PPARalpha, PPARgamma,
and LXR
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors (PPARs) are nuclear
receptors expressed in macrophages where they control cholesterol
homeostasis and inflammation. In an attempt to identify new
PPARalpha and PPARgamma target genes in macrophages, a DNA
array-based global gene expression profiling experiment was
performed on human primary macrophages treated with specific
PPARalpha and PPARgamma agonists. Surprisingly, AdipoR2, one
of the two recently identified receptors for adiponectin,
an adipocyte-specific secreted hormone with anti-diabetic
and anti-atherogenic activities, was found to be induced by
both PPARalpha and PPARgamma. AdipoR2 induction by PPARalpha
and PPARgamma in primary and THP-1 macrophages was confirmed
by Q-PCR analysis. Interestingly, treatment with a synthetic
LXR agonist induced the expression of both AdipoR1 and AdipoR2.
Furthermore, co-incubation with a PPARalpha ligand and adiponectin
resulted in an additive effect on the reduction of macrophage
cholesteryl ester content. Finally, AdipoR1 and AdipoR2 are
both present in human atherosclerotic lesions. Moreover, AdipoR1
is more abundant than AdipoR2 in monocytes and its expression
decreases upon differentiation into macrophages, whereas AdipoR2
remains constant. In conclusion, AdipoR1 and AdipoR2 are expressed
in human atherosclerotic lesions and macrophages and can be
modulated by PPAR and LXR ligands, thus identifying a mechanism
of crosstalk between adiponectin and these nuclear receptor
signaling pathways. |
| Chinetti
G, et al. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2004 Jan 30;314(1):151-8
|
| |
|
Growth hormone is a positive regulator of adiponectin receptor
2 in 3T3-L1 adipocytes
|
| The fat-derived
protein adiponectin is an important insulin-sensitizing adipocytokine
which is downregulated in insulin resistance and obesity.
Recently, two receptors of this adipose-expressed protein
called adiponectin receptor 1 (AdipoR1) and 2 (AdipoR2) have
been cloned. To clarify expression and regulation of these
receptors in fat cells, AdipoR1 and AdipoR2 mRNA was measured
by quantitative real-time reverse transcription-polymerase
chain reaction during differentiation of 3T3-L1 adipocytes
and after treatment with various hormones known to induce
insulin resistance. Interestingly, AdipoR2 synthesis was significantly
increased up to 4.8-fold during differentiation of 3T3-L1
preadipocytes, whereas AdipoR1 expression was only augmented
up to 1.4-fold. Furthermore, growth hormone (GH) induced AdipoR2,
but not AdipoR1 mRNA by up to 2.4-fold in a dose- and time-dependent
fashion with significant stimulation detectable at concentrations
as low as 5 ng/ml GH and as early as 2 h after effector addition.
The positive effect of GH on AdipoR2 expression could be reversed
by withdrawal of the hormone for 24 h. In contrast, other
key hormones involved in the regulation of insulin resistance
and energy metabolism such as insulin, isoproterenol, dexamethasone,
triiodothyronine, angiotensin 2, tumor necrosis factor alpha,
and interleukin-6 did not influence AdipoR1 and AdipoR2 synthesis
in vitro. Taken together, our results suggest that AdipoR2
expression is differentiation-dependent and selectively regulated
by GH implying a potential role of this hormone in adiponectin-associated
alterations of insulin sensitivity and energy homeostasis.
|
| Fasshauer
M, et al. FEBS Lett. 2004 Jan 30;558(1-3):27-32 |
|

|
Yamauchi
T, et al. Nature. 2003 Jun 12;423(6941):762-9 |
| |
|
 |
|
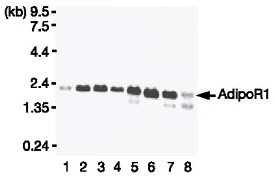
| Northern blot analysis
of AdipoR1 (left panel) and AdipoR2 (right panel) mRNA in
mouse tissues (lanes: 1, brain; 2, heart; 3, kidney; 4, liver;
5, lung; 6, skeletal muscle; 7, spleen; 8, testis). Yamauchi
T, et al. Nature. 2003 Jun 12;423(6941):762-9 |
|
|
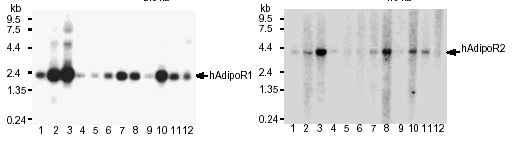
Northern blot analysis
of AdipoR1 (left panel) and AdipoR2 (right panel) mRNA in
human tissues (lanes: 1, brain; 2, heart; 3, skeletal muscle;
4, colon; 5, thymus; 6, spleen;7,kidney 8, liver;9,small intestine;
10, placenta; 11, lung; 12, peripheral blood leukocytes).
Yamauchi T, et al. Nature. 2003 Jun 12;423(6941):762-9 |
|

|
| 
|
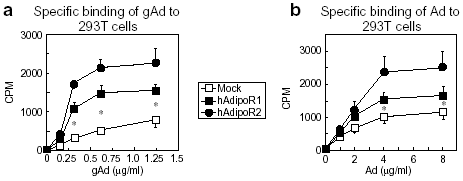
Effects of AdipoRs
expression on Adipo binding in 293 cells. Binding of [125I]
globular adiponectin (gAd) (a) or [125I] full-length adiponectin
(Ad) (b) to 293T transfected with AdipoR1 or AdipoR2.
Yamauchi T, et al. Nature. 2003 Jun 12;423(6941):762-9 |
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|


