- Gly-extended PYY (1-36) represents 20% of the total PYY in canine intestine;
- Gly-extended PYY (3-36) represents 6% of the total PYY in canine intestine;
We purified and identified the peptide YY (PYY) forms present and determined their levels from a portion of the canine ileum directly adjacent to the cecum by a new extraction method designed to prevent and evaluate degradation of endogenous peptides. We used three reverse phase chromatography steps with radioimmunoassay of fractions for PYY-like-immunoreactivity (PYY-LI). The purified fractions underwent intact protein/peptide mass spectrometry identification and sequencing (i.e. "top-down" MS analysis). This analysis confirmed the identity of a new form of PYY, PYY(1-36)-Gly, which co-elutes with PYY(1-36)-NH(2) through all three of separation steps used. The PYY(1-36)-Gly form represents approximately 20% of the total PYY found in this region of the canine intestine. In addition, we also found that the PYY(3-36)-NH(2) form represents 6% of the total PYY in the canine ileo-cecal junction. The physiological implication of the Gly-extended form of PYY(1-36) warrants further investigation.
Keire et al. Regul Pept. 2008 Nov 29;151(1-3):61-70.
Food intake is regulated by the hypothalamus, including the melanocortin and neuropeptide Y (NPY) systems in the arcuate nucleus. The NPY Y2 receptor (Y2R), a putative inhibitory presynaptic receptor, is highly expressed on NPY neurons in the arcuate nucleus, which is accessible to peripheral hormones. Peptide YY(3-36) (PYY(3-36)), a Y2R agonist, is released from the gastrointestinal tract postprandially in proportion to the calorie content of a meal. Here we show that peripheral injection of PYY(3-36) in rats inhibits food intake and reduces weight gain. PYY(3-36) also inhibits food intake in mice but not in Y2r-null mice, which suggests that the anorectic effect requires the Y2R. Peripheral administration of PYY(3-36) increases c-Fos immunoreactivity in the arcuate nucleus and decreases hypothalamic Npy messenger RNA. Intra-arcuate injection of PYY(3-36) inhibits food intake. PYY(3-36) also inhibits electrical activity of NPY nerve terminals, thus activating adjacent pro-opiomelanocortin (POMC) neurons. In humans, infusion of normal postprandial concentrations of PYY(3-36) significantly decreases appetite and reduces food intake by 33% over 24 h. Thus, postprandial elevation of PYY(3-36) may act through the arcuate nucleus Y2R to inhibit feeding in a gut-hypothalamic pathway.
Batterham et al. Nature 2002 Aug 8;418(6898):650-4
The distal gut hormone peptide YY (PYY) mediates feedback inhibition of gastric acid secretion, gastrointestinal motility, and pancreatic enzyme output. To investigate the influence of maldigestion on PYY, we determined plasma PYY levels in patients with celiac disease under basal conditions and in response to intraduodenal fat. Basal PYY was increased in untreated celiac patients (N = 13) compared to patients on a gluten free diet (N = 9) [15.6 (11.8-27.0) pM vs 12.2 (10.1-13.1) pM; P < 0.05] and compared to control subjects (N = 15) [9.5 (8.3-10.4) pM; P < 0.001]. Integrated PYY in response to intraduodenally infused predigested fat (1071+/-293 pM 80 min) was significantly (P < 0.05) greater than in response to undigested fat (322+/-223 pM 80 min) in six untreated celiacs. Plasma concentrations of PYY and cholecystokinin were strongly correlated (r = 0.79; P < 0.001). We conclude that basal PYY levels in untreated celiac disease are elevated, that predigestion of fat enhances PYY release in these patients, and that PYY secretion is correlated with CCK release.
Wahab et al. Dig Dis Sci 2001 Nov;46(11):2504-9
Neuropeptide Y (NPY), a 36-amino-acid peptide widely expressed in the brain is involved in many physiological responses, including hypothalamic control of food intake and cardiovascular homeostasis. NPY mediates its effects through binding to the Y1, Y2 and Y5 G-protein-coupled receptors. Little is known of the role of the Y2 receptor in mediating the different NPY effects. We inactivated the Y2 receptor subtype in mice and found that these mice developed increased body weight, food intake and fat deposition. The null mutant mice showed an attenuated response to leptin administration but a normal response to NPY-induced food intake and intact regulation of re-feeding and body weight after starvation. An absence of the Y2 receptor subtype also affected the basal control of heart rate, but did not influence blood pressure. These findings indicate an inhibitory role for the Y2 receptor subtype in the central regulation of body weight and control of food intake.
Naveilhan et al. Nat Med 1999 Oct;5(10):1188-93
Gastrointestinal transit was measured in non-obese diabetic (NOD) mice, as an animal model of human diabetes type 1, and in obese diabetic mice, as an animal model of human diabetes type 2. The endocrine cells known to correlate to gastrointestinal transit, namely secretin, serotonin, Peptide YY (PYY) and enteroglucagon cells, were identified by immunocytochemistry and quantified by computer image analysis in different segments of the gut. Gastrointestinal transit was significantly accelerated in NOD mice and slower in obese diabetic mice than in controls. The density of duodenal secretin and serotonin as well as colonic PYY and enteroglucagon cells in NOD mice was significantly higher than that of control mice. On the other hand, the density of duodenal secretin and serotonin cells was significantly lower in obese diabetic mice than in controls. It was concluded that changes in duodenal secretin and colonic serotonin, PYY and enteroglucagon cells may play a role in accelerated gastrointestinal transit in NOD mice and delayed gastrointestinal transit in obese diabetic mice.
El-Salhy. Ups J Med Sci 2002;107(1):23-33
Extracts of human term amniotic, placental, and chorion/decidua tissue contained, respectively, 4.36 +/- 2.79 (pmol/g wet wt; mean +/- S.E.M.: n = 5). 2.78 +/- 0.5 (n = 5) and 0.68 +/- 0.68 (n = 5) peptide YY (PYY)-like immunoreactivity. Using a specific PYY antiserum, gel filtration chromatography and reverse-phase high performance liquid chromatography (HLPC), amniotic, placental and fetal intestinal tissue extracts were demonstrated to contain PYY-like immunoreactivity consisting of equal amounts of PYY1-36 and PYY3-36. The presence of pancreatic polypeptide was not detected in any of the extracts. Positive immunohistochemical staining for PYY was seen in extravillous trophoblasts in the decidual septa and fetal membranes, the syncytiotrophoblast and cytotrophoblasts, amniotic epithelial cells and in maternal decidual stromal cells. Positive staining for PYY was found at the earliest date examined (9.5 weeks) and remained present throughout pregnancy to term. PYY1-36 and PYY3-36 may play important roles in human pregnancy, acting via endocrine or paracrine mechanisms.
Xiao et al. J Endocrinol 1998 Mar;156(3):485-92
The peptide YY derivatives [Leu31,Pro34]PYY and PYY3-36 are highly selective Y1 and Y2 agonists, devoid of activity on the Y3 receptor subtype [Dumont et al. (1994) Molec. Brain Res., 26:3220-3324]. These selective ligands were iodinated and used to evaluate the respective quantitative autoradiographic distribution of the Y1 and Y2 receptor subtypes in the rat brain, excluding a potential contamination from Y3 receptor. Specific [125I][Leu31,Pro34]PYY (Y1), and [125I]PYY3-36 (Y2) binding sites are detected in various brain regions, but each showed a differential distribution profile. Y1/[125I][Leu31,Pro34]PYY sites are especially concentrated in superficial layers of the cortex, the olfactory tubercle, islands of Calleja, tenia tecta, molecular layer of the dentate gyrus, several thalamic nuclei, and the posterior part of the medial mammaliary nucleus. These areas generally contained only low densities of Y2/[125I]PYY3-36 binding sites. In contrast, [125I]PYY3-36 binding is most abundant in multiple other regions including the lateral septum, piriform cortex, triangular septal nucleus, bed nucleus of the stria terminalis, oriens layer and stratum radiatum of the dorsal hippocampus, ventral tegmental area, substantia nigra, dorsal raphe nucleus, and the granular cell layer of the cerebellum. Few areas of the rat brain contained significant amounts of both [125I][Leu31,Pro34]PYY and [125I]PYY3-36 binding sites such as the anterior olfactory nuclei, oriens layer and stratum radiatum of the ventral hippocampus, nucleus tractus solitarius, area postrema, and inferior olive. Taken together, these results and the use of two selective radioligands demonstrate further the discrete, differential distribution of the Y1 and Y2 receptor subtypes in the rat brain.
Dumont et al. Synapse 1996 Feb;22(2):139-58
The peptide YY (PYY)-derivatives [Leu31,Pro34]PYY and PYY3-36 were respectively developed as selective Y1 and Y2 radioligands devoid of affinity for the Y3 receptor subtype. Each analog was iodinated by the chloramine T method after a purification by reverse-phase high-performance liquid chromatography. Both radioligands bind with high affinity, low capacity and in a time-dependent and saturable manner to specific sites present in rat frontoparietal cortical or hippocampal membrane preparations. [125I][Leu31,Pro34]PYY demonstrated apparent affinities (Kd) of 0.42 +/- 0.07 and 0.22 +/- 0.08 nM and maximal capacities (Bmax) of 185 +/- 14 and 33 +/- 4 fmol/mg of protein to a single class of sites in cortical and hippocampal membrane homogenates, respectively. Conversely, [125I]PYY3-36 apparently bound to a greater amount of sites in hippocampal (Bmax of 109 +/- 13 fmol/mg of protein; Kd of 0.13 +/- 0.03 mM) compared with cortical (Bmax of 33 +/- 5 fmol/mg of protein; Kd of 0.37 +/- 0.06 nM) membrane preparations, which suggests the differential enrichment of these two brain regions with a given neuropeptide Y (NPY) receptor subtype. The comparative ligand selectivity profile of these two radiolabeled PYY derivatives confirmed this hypothesis and revealed that, although the rat frontoparietal cortex is enriched with Y1 sites, Y2, receptor binding sites are most abundant in the hippocampus.
Comparative binding of 125I-PYY3-36 to rat hippocampal and cortical membrane |
| |
Bmax |
Kd |
| Rat Hippocampal membrane homogenate |
109 ± 13 fmol/mg Protein |
0.13 ± 0.03 mM |
| Rat cortical membrane homogenate |
33 ± 5 fmol/mg Protein |
0.37 ± 0.06 mM |
Dumont et al. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 1995 Feb;272(2):673-80

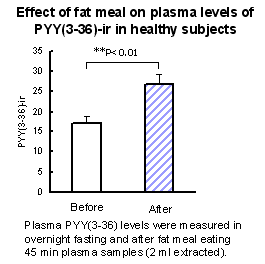
Plasma PYY(3-36) levels were measured in normal subjects (n=8) in two blood draws. The first draw was taken after overnight fast, and the second was taken 45 minutes after a large meal. ( results were obtained using 2 ml of extracted plasma). |


